
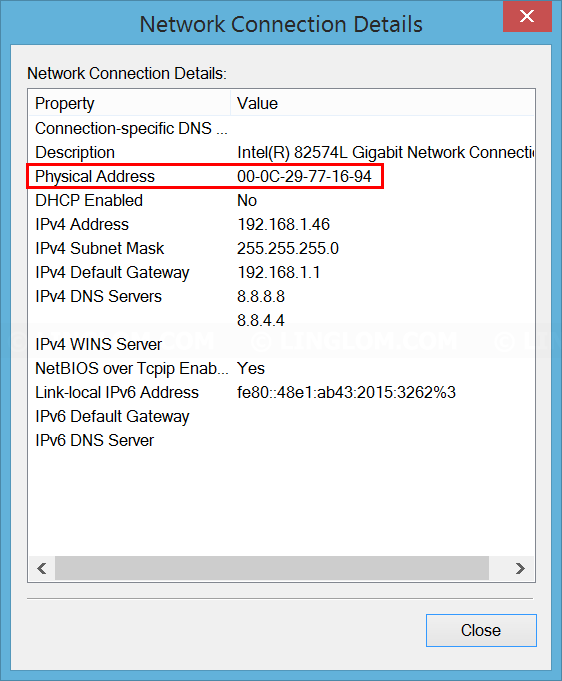
This topology will illustrate how it works: The item which tells a host whether another IP address is on the same network or a different network is the subnet mask. If a host is speaking to another host on a different IP network, the target for the ARP request will be the Default Gateway’s IP address. The original thought process for Proxy ARP was to accommodate hosts with misconfigured subnet masks.Īs we’ve discussed before, when a host is speaking to another host on the same IP network, the target for the ARP request is the other host’s IP address. Proxy ARP is not a malicious event, it occurs to enable connectivity between two hosts that wouldn’t otherwise be possible. Proxy ARP occurs when one node is responding to an ARP request on behalf of another node. In this article we will discuss Proxy ARP and its role and significance.
We’ve discussed the use cases and role of traditional ARP in the prior article of this series. Use the navigation boxes to view the rest of the articles.

This article is a part of a series on Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
